Blog 10-30-22
1 Install Nginx and related stacks on CentOS 8
1.1 Automated Script
I use HocVPS Script to simplify the installation process, allowing for simple management in the future.
HocVPS Script will support:
- Centos 7
- Centos 8
- Rocky Linux 8
- Ubuntu 18.04
- Ubuntu 20.04
HocVPS Script will automatically install:
- Webserver nginx latest version.
- The latest version of database MariaDB (MySQL is optimized).
- Option to install and update New Mariadb versions during setup
- PHP latest version options: PHP 8.0, PHP7.4, PHP 7.3, PHP 7.2, PHP 7.1, PHP 7.0, PHP 5.6; comes Zend OPcache which makes - PHP work fastest
- latest phpMyAdmin
- the latest eXtplorer to manage File Manager, can create user, separate permissions
- Option to install firewall using CSF
- Support to install let’s Encrypt SSL certificate for website
- Supports installation of commercial SSL certificates (Sectigo, Geotrust, IDE)
Run the following command to install:
curl -sO https://hocvps.com/install && bash installWhen the prompt to enter your email appears, just input your working email.
THen enter PHP version that you want to use. I choose the latest PHP 8.0
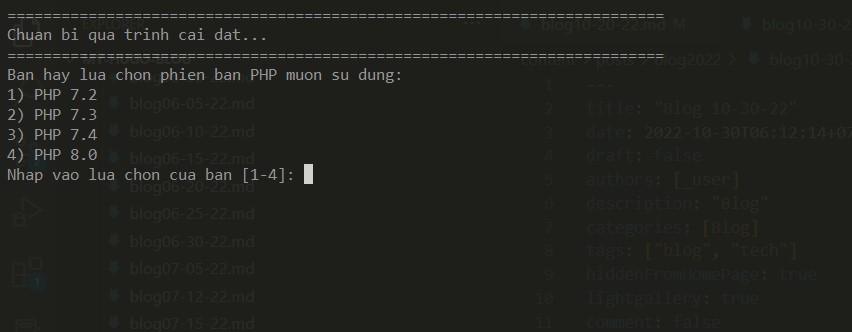
Enter your domain, for example: pquan.info
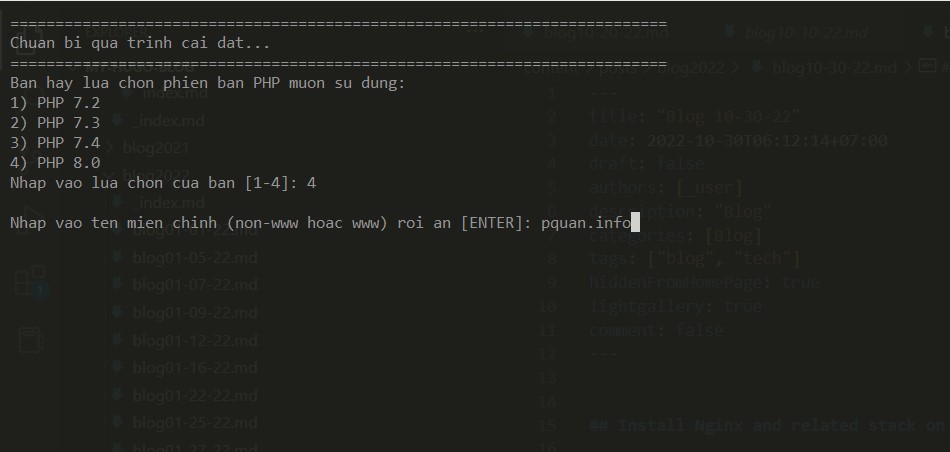
Then enter your secret desired port admin, which is from the range of (2000 – 9999), can be change later. It’s used for these following stuff:
- Access the admin link, in the form of:
http://domain.com:port/ - Using phpMyAdmin, link form:
http://domain.com:port/phpmyadmin/ - File Manager, link form:
http://domain.com:port/filemanager/ - Monitor System Status, link form:
http://domain.com:port/serverinfo/ - Track Zend Opcache Status, link form:
http://domain.com:port/op.php
You’ll be ask to specify MariaDB version:
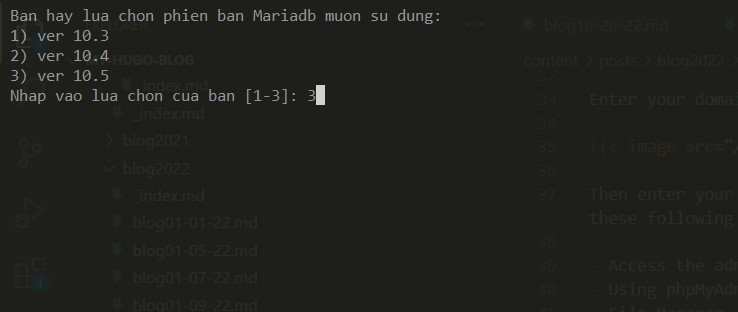
After that, you let the script automatically perform the installation process, which can take 3-5 minutes depending on the configuration and network of the VPS / Server.
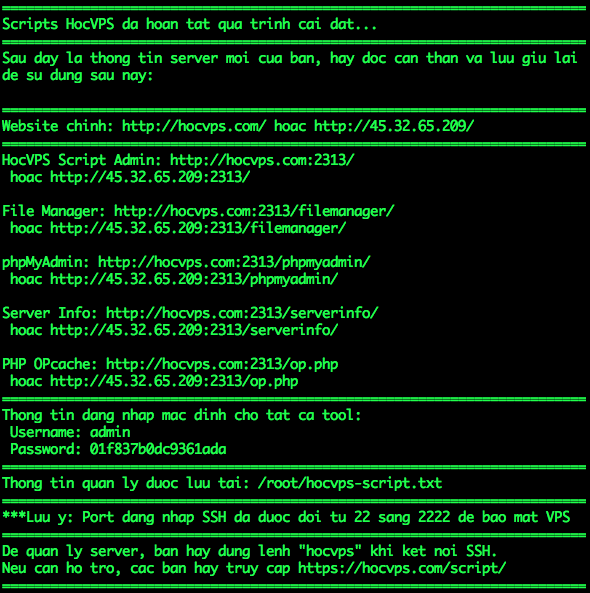
Finally, if no problem occurs, you will receive successful installation notifications and VPS management information as below. At the same time, this information will also be saved in the text file with the path /root/hocvps-script.txt for you to review later.
1.2 How to use the script
After installing hocvps Script, you can use SFTP to manage files, upload code to /home/domain.com/public_html/ and point the domain name to IP of the VPS and start using.
Run hocvps to access the script menu.
hocvpsNote: after uploading the source to the web folder, you use Hocvps menu 14 Webserver permissions for NGINX to read the website content.
If you want to connect to SSH, use port 2222.
During use, being in any function you can press Ctrl + C will exit the Script immediately.
1.3 Installing the latest Nginx version
Create the following file:
nano /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo After that add the following content which specifies the Nginx repository which we will use to install the latest Nginx version:
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
[nginx-mainline]
name=nginx mainline repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=trueSave the file and exit. Then run hocvps script.
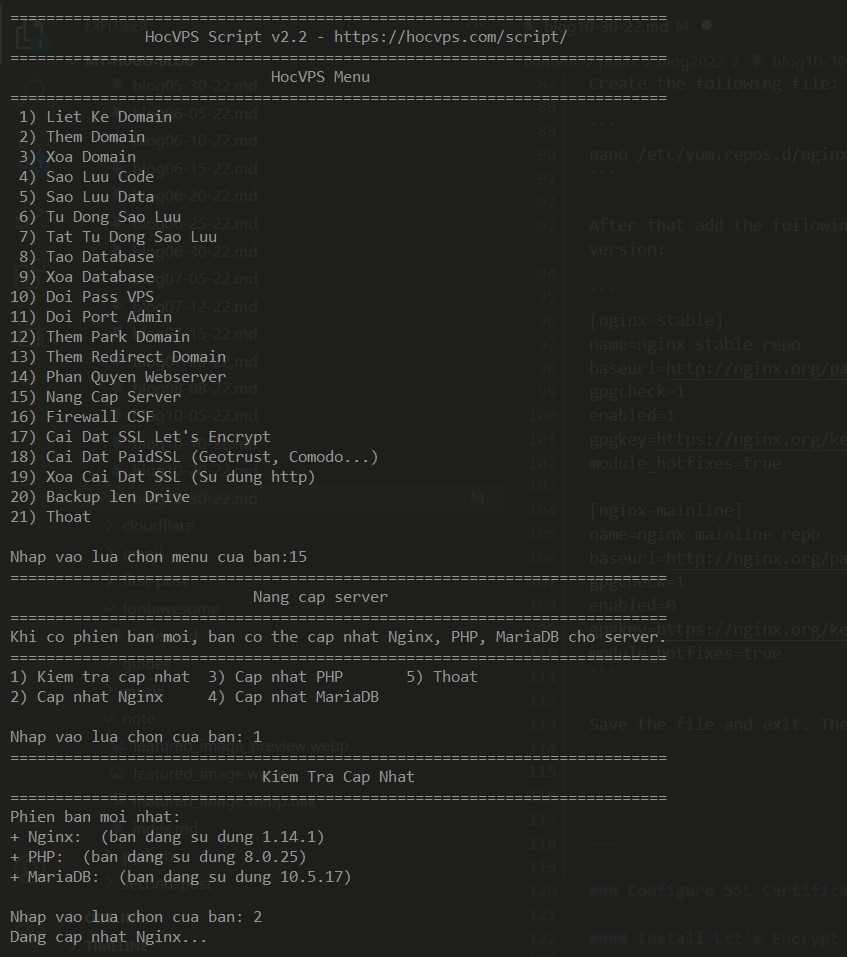
Choose menu 15, then select option 2 to update Nginx to latest stable version.
1.4 Configure SSL Certificate for your domain
1.4.1 Install Let’s Encrypt
Install Certbot:
yum -y install certbotIssue Let’s Encrypt for domain:
# Stop Nginx
service nginx stop
# Issue SSL Let's Encrypt
certbot certonly --standaloneNext you enter the domain name that will use the SSL certificate, and then press Enter. This step you only enter the non-www And www versions of 1 domain or subdomain.
1.4.2 Nginx Configuration
Create a DH Parameters 2048 bit file:
mkdir /etc/nginx/ssl/
openssl dhparam -out /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem 2048Note: When the number of bits, in this case 4096, comes after the option where to put the file (-out), openssl seems to output meaningful data. That is the correct way. The script may fail to create a param file, if you put the option after the numbits, be it 512, 2048 or 4096.
Modify the domain cofiguration by editing yourdomain.com.conf:
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/yourdomain.com.confConfiguring SSL processing requests
In the block server { … } adjustment as follows:
Convert listen 80 default_server to listen 443 ssl default_server;
After the server_name yourdomain.com added SSL configuration snippet:
# SSL
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/hocvps.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/hocvps.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_ciphers EECDH+CHACHA20:EECDH+AES128:RSA+AES128:EECDH+AES256:RSA+AES256:EECDH+3DES:RSA+3DES:!MD5;
# Improve HTTPS performance with session resumption
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
# DH parameters
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem;
# Enable HSTS
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000" always;:(fas fa-star-of-life): The Nginx configuration file will be similar to the following:
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name www.yourdomain.com;
# SSL
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/yourdomain.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/yourdomain.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_ciphers EECDH+CHACHA20:EECDH+AES128:RSA+AES128:EECDH+AES256:RSA+AES256:EECDH+3DES:RSA+3DES:!MD5;
rewrite ^(.*) https://yourdomain.com$1 permanent;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name yourdomain.com www.yourdomain.com;
rewrite ^(.*) https://yourdomain.com$1 permanent;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
# access_log off;
access_log /home/yourdomain.com/logs/access.log;
# error_log off;
error_log /home/yourdomain.com/logs/error.log;
root /home/yourdomain.com/public_html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
server_name yourdomain.com;
# SSL
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/yourdomain.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/yourdomain.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_ciphers EECDH+CHACHA20:EECDH+AES128:RSA+AES128:EECDH+AES256:RSA+AES256:EECDH+3DES:RSA+3DES:!MD5;
# Improve HTTPS performance with session resumption
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
# DH parameters
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem;
# Enable HSTS
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000" always;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
# Custom configuration
include /home/yourdomain.com/public_html/*.conf;
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 1000;
fastcgi_send_timeout 1000;
fastcgi_read_timeout 1000;
fastcgi_buffer_size 256k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 256k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 256k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 256k;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /home/hocvps.com/public_html$fastcgi_script_name;
}
location /nginx_status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny all;
}
location /php_status {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /home/hocvps.com/public_html$fastcgi_script_name;
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny all;
}
# Disable .htaccess and other hidden files
location ~ /\.(?!well-known).* {
deny all;
access_log off;
log_not_found off;
}
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location ~* \.(3gp|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|ico|wmv|avi|asf|asx|mpg|mpeg|mp4|pls|mp3|mid|wav|swf|flv|exe|zip|tar|rar|gz|tgz|bz2|uha|7z|doc|docx|xls|xlsx|pdf|iso|eot|svg|ttf|woff)$ {
gzip_static off;
add_header Pragma public;
add_header Cache-Control "public, must-revalidate, proxy-revalidate";
access_log off;
expires 30d;
break;
}
location ~* \.(txt|js|css)$ {
add_header Pragma public;
add_header Cache-Control "public, must-revalidate, proxy-revalidate";
access_log off;
expires 30d;
break;
}
}2 Installing Iptables on CentOS
HocVPS Script will also install iptables. So you can skip installing steps and go straight to iptables Commands and Options.
In CentOS, iptables was replaced by firewalld.
To install iptables, first you need to stop firewalld. Enter the following commands:
sudo systemctl stop firewalld
sudo systemctl disable firewalld
sudo systemctl mask firewalldThe commands stop and prevent firewalld from starting at boot, and do not let other services start firewalld.
Next, install and enable iptables. First, install the iptables services package with the following command:
sudo yum -y install iptables-servicesEnter the following commands to enable and start iptables in CentOS:
sudo systemctl enable iptables
sudo systemctl start iptables2.1 Basic Syntax for iptables Commands and Options
In general, an iptables command looks as follows:
sudo iptables [option] CHAIN_rule [-j target]Here is a list of some common iptables options:
-A –append – Add a rule to a chain (at the end). -C –check – Look for a rule that matches the chain’s requirements. -D –delete – Remove specified rules from a chain. -F –flush – Remove all rules. -I –insert – Add a rule to a chain at a given position. -L –list – Show all rules in a chain. -N -new-chain – Create a new chain. -v –verbose – Show more information when using a list option. -X –delete-chain – Delete the provided chain.
2.2 Check Current iptables Status:
To view the current set of rules on your server, enter the following in the terminal window:
sudo iptables -L2.3 Enable Loopback Traffic:
It’s safe to allow traffic from your own system (the localhost). Append the Input chain by entering the following:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT2.4 Allow Traffic on Specific Ports:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPTThe options work as follows:
-p – Check for the specified protocol (tcp). –dport – Specify the destination port. -j jump – Take the specified action.
2.5 Delete a Rule:
You can use the -F option to clear all iptables firewall rules. A more precise method is to delete the line number of a rule.
First, list all rules by entering the following:
sudo iptables -L --line-numbersLocate the line of the firewall rule you want to delete and run this command:
sudo iptables -D INPUT <Number>2.6 Save Your Changes:
Iptables does not keep the rules you created when the system reboots. Whenever you configure iptables in Linux, all the changes you make apply only until the first restart.
To save the rules in Debian-based systems, enter:
sudo /sbin/iptables–saveTo save the rules in Red-Hat based systems, enter:
sudo /sbin/service iptables saveThe next time your system starts, iptables will automatically reload the firewall rules.